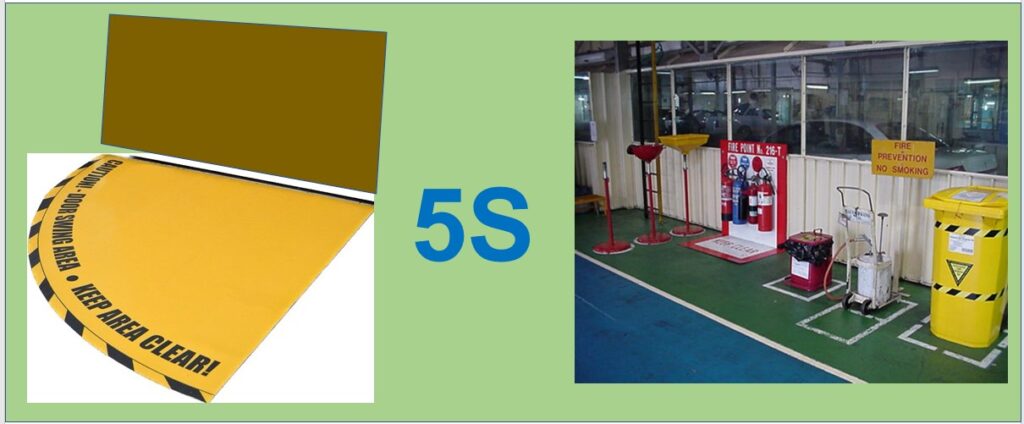
WHAT ?
5S is a workplace organization technique composed for five primary phases – Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize and Systematize.
With the ever-changing economic climate, many organizations are periodically adjusting their resources to align with business strategy.
This often results in the need to achieve more work with fewer resources. In order to remain successful, businesses must become more efficient, reduce waste and thereby reduce cost. We must find ways to do what we are currently doing in less time and at a lower cost. One way we can accomplish this is through the use of 5S Principles. The 5S Principles are very effective at identifying and eliminating waste and increasing efficiency. There is a lot of information about 5S and how it came to be.
The popular belief is that the Japanese invented the 5S Methodology because the letter “S” stands for five Japanese words, that when translated to roman script, start with the letter “S”.
In actuality, the principles within 5S were being utilized decades before by Mr. Henry Ford. It has been reported that prior to 1920, Mr. Ford was using CANDO in his manufacturing processes. The acronym CANDO stands for Cleaning up, Arranging, Neatness, Discipline and Ongoing improvement.
In the 1950s, representatives from Toyota visited the Ford facilities to be trained in automotive mass production methods. The Japanese later adapted the CANDO methods and applied them in their production facilities. Some commonly used words describing the steps in 5S are Sort, Set, Shine, Standardize and Sustain. Throughout different companies, various words are used that have similar meanings. No matter what specific words are used to identify the steps in 5S, the purpose remains the same: create a clean, organized and efficient work environment.
Let us understand all five principles in details:
[1]. SORT: KEEP ONLY NECESSARY ITEMS IN THE WORKPLACE
PRINCIPLES
- Review tools, Parts & Instructions
- Keep only what is essential
- Eliminate anything those are all unwanted, Unessential items
EXAMPLES
- Obsolete or expired procedures
- Damaged or obsolete inventories, old machinery
- Mixed scrap in the yard
[2]. SET IN ORDER: ARRANGE ITEMS TO PROMOTE EFFICIENT WORK FLOW
PRINCIPLES
- Arrange items in logical order
- Indicate places for each item clearly
- Each item close to where it will be used.
EXAMPLES
- Excess movement, Waste of movements & motion
- Excess transportation
- Over processing
- Over production
- Excess inventory
- Excess delays
- Defects
[3]. SHINE: CLEAN THE WORK PLACE OR AREA, SO IT IS NEAT & TIDY
PRINCIPLES
- Make cleaning a part of daily work
- Assign areas of responsibility
- Return all items or files to their assigned place
EXAMPLES
- Dirty tools & equipments
- Scrap over flow
- Aisle not clear & dirty
- Clutter & mess
[4]. STANDARDIZE: SET STANDARD FOR CONSISTENTLY ORGANIZED WORKPLACE
PRINCIPLES
- Create standards for Sort, Set in order & Shine
- Make standards easy to understand with proper visual controls
- Assign the standardized activities to each individuals & make them responsible to comply
- Regular review of standard & if required revise it
EXAMPLES
- Work instructions of work stations, work cells, departments
- Hazard warnings
- Equipment / Tools labels, Storage labels
- Process diagrams
- SOPs
[5]. SYSTEMATIZE: MAINTAIN & REVIEW STANDARDS
PRINCIPLES
- Measure & monitor process
- Address root causes and avoid reversion to the ‘old ways’
- Promote individual feedback and response for improvements
EXAMPLES
- Emphasize cooperation
- Communicate clearly
- Support innovation
(In future, article we will go though all the topics in depth understanding)
_______________ XXXXX ______________
Note: Above views are purely written based on my own individual experience through various industries & based on that above points have been came out. Also gone through various books & Reference sites before conclude. Hence before implementing, pls. review & decide whether it suits/align to your requirements or not.